Difference between revisions of "Deschampsia cespitosa"
(→Description) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
(→Uses) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
Tufted hairgrass is frequently grazed by bears. Sitka black-tailed deer and feral horses consume tufted hairgrass. Larval host and/or nectar source for Umber Skipper. Attracts birds. | Tufted hairgrass is frequently grazed by bears. Sitka black-tailed deer and feral horses consume tufted hairgrass. Larval host and/or nectar source for Umber Skipper. Attracts birds. | ||
| − | First Nations people report that seeds of Deschampsia species | + | First Nations people report that seeds of Deschampsia species have been eaten by indigenous peoples of California and Utah.<ref>Native American Ethnobotany Database. Retrieved from http://naeb.brit.org/uses/12331/</ref> |
===Propagation=== | ===Propagation=== | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 29 March 2021
- Scientific Name: Deschampsia cespitosa
- Family: Poaceae
- Common Names: Bering hair grass, Pacific hair grass, tufted hair grass, Beringian hairgrass, tufted hairgrass
- Synonyms/Misapplications: Aira caespitosa, Aira holciformis, Deschampsia beringensis, Deschampsia caespitosa, Deschampsia glauca, Deschampsia holciformis
- Codon: DESCES
Contents
Taxonomy
| Scientific classification | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Subkingdom: | Viridiplantae |
| Phylum: | Tracheophyta |
| Subphylum: | Spermatophytina |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: | Lilianae |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Deschampsia P. Beauv. |
| Species: | Deschampsia cespitosa (L.) P. Beauv. |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Description
Tufted hairgrass is a densely cespitose cool-season native perennial bunchgrass. Culms are hollow, slender, erect, and 8 to 48 inches (20-120 cm) in height.
Abundant leaves form basal tufts; blades are 0.8 to 13 inches (2-33 cm) long and 0.04 to 0.16 inch (1-4 mm) wide.
The inflorescence is generally a loose, open panicle, though occasionally narrow and contracted; it is 4 to 12 inches (10-30 cm) long.
Branches are whorled, hairlike, and spikelet-bearing near their tips. Spikelets are two- to occasionally three-flowered. Lemmas are awned toward the base. The fruit is a caryopsis.[2]
Bloom Period
Blooms in June to September.[3]
Distribution
Widely distributed on both sides of the Cascades crest in Washington; Alaska to California, east to the northern Great Plains, Great Lakes region, and eastern North America.[3]
Habitat
Deschampsia cepitosa occurrence is circumglobal, extending throughout cooler regions of the northern Hemisphere. In Oregon and Washington, sites with tufted hairgrass include seasonally wet soils in low lying areas of the western interior valleys, tidal mudflats and estuarine plant communities near the coast, poorly drained fields, and moist mountain meadows. It can form nearly pure stands in wet or intermittently flooded areas. The species is highly variable.
Occurs in fine, medium and coarse soils – sandy loam, sandy clayey loam, silty loam, loam, loamy clay, and clay. Tufted hairgrass growth is rated fair on sandy loam and good on loam and clayey loam.[4]
Uses
Tufted hairgrass is frequently grazed by bears. Sitka black-tailed deer and feral horses consume tufted hairgrass. Larval host and/or nectar source for Umber Skipper. Attracts birds.
First Nations people report that seeds of Deschampsia species have been eaten by indigenous peoples of California and Utah.[5]
Propagation
Tufted hairgrass can be grown for seed on well drained medium to fine textured soils on uplands as well as on poorly-drained silts and clays in low lying areas. If seasonally flooded areas are to be used for seed production, fields must be firm enough to perform weed control measures and dry enough to windrow and harvest by as early as mid-June (western Oregon). This species is broadly adapted to soils that are acid to neutral (pH 4.5-7.0).[6]
Good results from fall sowing. In a nursery, sow in containers in April on heat (night -15º C, days 20-24º C), germination in 30 days. Cover lightly with soil and screen until germination occurs. Plugs form slowly in about 60 days if kept continually moist and at a constant temperature (S. Bastin, pers. comm.).
Can be very aggressive. Leave room to spread or control in place. Doesn't tolerate transplanting unless well-rooted (S. Bastin, pers. comm.).
Seed
Average Measurement with husk/awn: 3.4 x 0.8 x 0.8
Average Measurement without husk/awn: 1.8 x 0.6 x 0.6
Measurement Range with husk/awn: L: 2.5 – 4.5, W: 0.5 – 1, D: 0.6 – 1
Measurement Range with husk/awn: L: 1.5 – 2, W: 0.5 – 0.75, D: 0.5 – 0.6
Features
Shape: Seed narrow at hilum and opposite apex, rounded in the middle.
Additional Structures: Lemma thin, and have several nerves running across them. Awn originates from the hilum and is about 1 ½ times the length of the seed body. Hilum bearded with feather like appendage. Palea also thin.
Color: Tan palea and lemma, awn slightly darker brown. Inner seed red-brown, and somewhat transparent.
Surface: Seed finely longitudinally striate and lustrous. Awn finely barbed.
Latitudinal Cross Section: elliptical 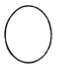
Longitudinal Cross Section: elliptical ![]()
Photo Gallery
References
- http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=DECE
- http://biology.burke.washington.edu/herbarium/imagecollection.php
- http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=DECE
- http://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/graminoid/desces/introductory.html
- ↑ Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved from https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=502001
- ↑ USFS Fire Effects Information System. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/database/feis/plants/graminoid/desces/all.html
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 WTU Herbarium, Burke Museum, & University of Washington. Retrieved from http://biology.burke.washington.edu/herbarium/imagecollection/taxon.php?Taxon=Deschampsia%20cespitosa
- ↑ USDA Plant Material Technical Note 16. Retrieved from https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_PLANTMATERIALS/publications/orpmctn0578.pdf
- ↑ Native American Ethnobotany Database. Retrieved from http://naeb.brit.org/uses/12331/
- ↑ USDA Plant Guide. Retrieved from https://plants.usda.gov/plantguide/pdf/pg_deca18.pdf


