Difference between revisions of "Leptosiphon bicolor"
m (Tag: VisualEditor) |
m (→Photo Gallery) (Tag: VisualEditor) |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
'''Longitudinal cross section:''' elliptical [[File:LEBI long.png]] , and at times, obovate [[File:LEBI long ob.png]] | '''Longitudinal cross section:''' elliptical [[File:LEBI long.png]] , and at times, obovate [[File:LEBI long ob.png]] | ||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| − | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| − | File: | + | File:LEPBIC2.jpg|Photo by Ray Izumi, 2013 |
| − | File:LEBI | + | File:LEBI LisaHintz sd 2012.jpg|Photo by Lisa Hintz |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === References === | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:28, 9 June 2020
- Latin Name: Leptosiphon bicolor
- Family: Polemoniaceae
- Common Names: bicolored babystars, bicolored linanthus
- Synonyms/Misapplications: Linanthus bicolor
- Codon: LEPBIC
Contents
Taxonomy
| Leptosiphon bicolor | |
|---|---|

| |
| photo by Ben Legler, also featured on Main Page | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Subkingdom: | Tracheobionta |
| Phylum: | Spermatophyta |
| Subphylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Subclass: | Asteranae |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Polemoniaceae |
| Genus: | Leptosiphon Benth. |
| Species: | Leptosiphon bicolor var. Nutt. |
Description
General: Slender annual up to 1.5 dm. tall, the stem puberulent, often branched at the base, otherwise usually simple.
Leaves: Leaves rather firm, palmately 3-7 cleft, up to 2 cm. long, the segments linear, harshly ciliate.
Flowers: Flowers fragrant, sub-sessile in a dense, terminal, leafy cluster, the inflorescence leaves longer and more prominently ciliate than the lower; calyx firm, 5-10 mm. long, the 5 segments with needle-like tips; corolla with a very slender tube up to 3 cm. long, the throat yellow, the 5 abruptly-flaring, short lobes deep pink to purplish or white; stamens 5, the filaments attached in the corolla throat; style 3-parted; ovary superior.
Fruit: Capsule with 3, several-seeded carpels.
Bloom Period
April- June[1]
Distribution
West of the Cascades, Vancouver Island, B. C., to California, east through the Columbia Gorge
Habitat
Mesic to dry, open, grassy places in the lowland zone; locally frequent on S Vancouver Island and the Gulf Islands; S to CA.
Uses
None found (at the moment)
Propagation
Seeds were sown into cone-tainers filled with Sunshine # 1 (a soil-less, peat-based media) amended with micro-nutrients (Micromax) and a slow-release fertilizer (Osmocote 14-14-14). Flats of conetainers were placed in greenhouse set at moderate temperatures (70 degree days/50 degree nights.) Seeds germinated readily with no treatment. Most seeds germinated within one to two weeks. (Leptosiphon grandiflorus also needed no treatment before germination).
http://biology.burke.washington.edu/herbarium/imagecollection.php
http://plants.usda.gov/java/nameSearch
Seed
Seed sample from: 2011
Average Measurement: 1.3 x 0.8 x 0.7
Measurement Range: L: 1.1 – 1.75, W: 0.6 – 1, D: 0.5 – 1
Features
Shape: Seeds somewhat tear shaped, others elliptical.
Color: Seeds partially translucent and brown. Hilium inconspicuous.
Surface: Seeds bumpy and somewhat corrugated, giving them a “brain-like” texture. Seeds slightly glossy.
Latitudinal Cross Section: elliptical 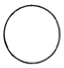
Longitudinal cross section: elliptical ![]() , and at times, obovate
, and at times, obovate ![]()
Photo Gallery
References
- ↑ WTU Herbarium, Burke Museum, & University of Washington. Retrieved from https://biology.burke.washington.edu/herbarium/imagecollection/taxon.php?Taxon=Leptosiphon%20bicolor



